Bone Marrow Transplant Hospital in Mumbai, India
Bone Marrow Transplant Hospital in Mumbai, India
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure that replaces damaged or diseased bone marrow cells with healthy blood-forming stem cells. A bone marrow transplant is also called a stem cell transplant or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). It is performed when the bone marrow stops working and does not produce healthy blood cells.
Fortis Hospitals Mumbai, India, Bone Marrow Department provides comprehensive care for patients of all age groups requiring bone marrow transplantation to treat a variety of blood disorders including cancers. Our transplant team comprises experts with extensive experience in performing modern transplantation techniques for adults and children, such as autologous transplant (with the patient’s cells), allogeneic transplant (with donor cells), and cord blood transplant (with umbilical cord cells). Centre’s state-of-the-art bone marrow transplant facility utilizes a collaborative approach, working across departments like hematology, infectious diseases, oncology, and pediatrics, to provide customized care to patients based on their clinical condition, for example, a bone marrow transplant can also be performed as an outpatient procedure at the hospital.
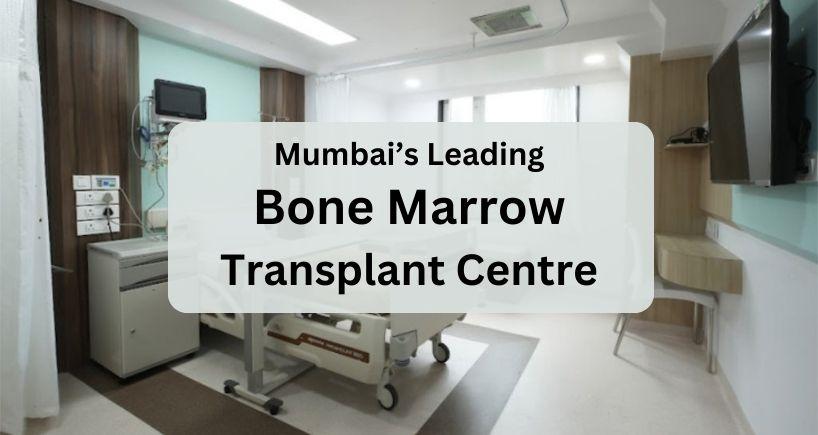
The 6-bedded unit is the largest such unit in the eastern suburbs of the city. The infrastructure in this wing has been planned and executed, keeping the patient at the center of care. The design is of international standards incorporating world-class, robust infection control practices.
Best Hospital for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation in India
Each room has its own Air Handling Unit (AHU) with an automatic and selective control system that creates positive air pressure inside the room. Thus, no outside air is allowed to enter the patient’s room, ensuring infection prevention. The HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters installed can absorb the minutest of particles like pollen, dust, moisture, bacteria, virus, etc. helping to maintain a purified environment.
Every room functions like an independent intensive care unit, fully equipped with a centralized oxygen and suction system, and six parameter monitors for monitoring heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, central venous pressure, ECG, infusion, and syringe pumps.
We are one of the leading hospitals in India for the best surgical outcomes, at par with international standards. Pivotal to our bone marrow transplant program is the psychosocial and mental well-being support, health education, and advanced care accessible to the patient and the family throughout the clinical journey. The patient is actively involved in understanding the risks and benefits of the care plan, to enable a smooth transition post-transplant, to lead a longer, better quality of life.
What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are special cells with the ability to make copies of themselves and change into different kinds of cells that the body needs. They can be found in different parts of the body at different times. Hematopoietic stem cells are stem cells that turn into blood cells. The bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue found in most bones of the body and it contains hematopoietic stem cells. These cells are also found in the blood that is moving throughout the body. Cancer and cancer treatment can damage hematopoietic stem cells; this means they may not turn into red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
- Blood cells are crucial and they perform the following functions in our body:
- Red blood cells - transport oxygen throughout the body. They also carry carbon dioxide to the lungs so it can be exhaled.
- White blood cells - are a part of the immune system and fight disease-causing viruses and bacteria.
- Platelets - help in forming clots to stop bleeding.
The bone marrow transplant procedure replaces healthy stem cells in the blood, thereby restoring the body’s ability to create the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, that it requires.
When is a Bone Marrow Transplant Needed?
Cancer and treatment for cancer can damage stem cells in the body. A hematopoietic stem cell transplant is used to:
- Safely continue treatment for clinical conditions requiring high doses of chemotherapy or radiation, by replacing the damaged bone marrow.
- Replace the damaged/diseased bone marrow with new stem cells.
- Supply new stem cells, which can help kill cancer cells directly.
Bone marrow transplantation technique can benefit patients with a variety of benign and malignant cancers, including:
- Leukemias
- Severe aplastic anemia
- Lymphomas
- Multiple myeloma
- Immune deficiency disorders
What are the Different Types of Bone Marrow Transplants?
There are different types of bone marrow transplants. The two main types of transplants depend on who serves as the donor.
1. Autologous transplant
Uses an infusion of the patient’s stem cells to restore the body’s ability to make healthy blood cells. In this procedure, there is no need to check for compatibility, unlike the donor transplant. This option is used when the body is producing enough healthy bone marrow cells, which can be collected, frozen, and stored for later use.
Autologous transplant is used to treat:
- Multiple myeloma
- Relapse lymphoma
2. Allogeneic transplant
uses donor cells to provide patients with new blood cells after cancer treatment. Finding a donor match is a necessary step for an allogeneic transplant. A healthy donor’s blood proteins called human leukocyte antigens (HLA) should closely match with the patient. Siblings from the same parents are often the best match, but another family member or an unrelated person can be a match too.
The blood stem cells used in an allogeneic stem cell transplant can be collected from the:
- donor's blood
- the bone marrow of the donor's hipbone
- blood of a donated umbilical cord
Allogenic transplant is used to treat:
- Acute Leukaemia
- Aplastic Anaemia
- Bone marrow failure disease
- Thalassemia
Preparation for a Bone Marrow Transplant
If the preferred mode of treatment for the patient is a bone marrow transplant, a series of tests are conducted to evaluate the patient’s clinical condition such as:
- Blood tests (including exposure to Hepatitis and HIV)
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Heart test (ECG)
- Lung tests (pulmonary function tests)
- Chest x-ray
- Dental x-ray
Also, a surgeon or a radiologist implants a long thin tube (intravenous catheter) into a large vein in the patient’s chest or neck. The catheter (often called a central line) usually remains in place for the duration of the entire treatment and is used by the transplant team to infuse transplanted stem cells, medications, and blood products into the patient’s body.
Bone Marrow Transplant Techniques
The bone marrow transplant begins with a preparation therapy called conditioning that includes chemotherapy, with or without radiation. This is done to destroy cancer cells, suppress the immune system, and prepare the body for new bone marrow cells. The stem cells are collected for the transplant before the conditioning process begins:
◈ Stem cells are collected from a patient or donor’s blood in a procedure that’s similar to blood donation. This process is called apheresis. The blood is collected from the vein through the earlier-placed catheter.
◈ The blood spins through the apheresis machine that selects the stem cells, rest of the blood is returned to the patient or the donor through the catheter.
◈ In case the patient’s stem cells are to be infused, the stem cells are frozen and stored until needed. In the case of donor-donated stem cells, infusion happens on the day they are collected.
The conditioning and transplant may be done as an outpatient or inpatient procedure. Periodic transfusions of red blood cells and platelets may also be needed until the patient’s bone marrow starts producing enough of those cells on its own. In time, the new stem cells begin producing healthy blood cells. This process is called engraftment. It may take several weeks for the number of blood cells to return to normal.
Post the transplant, the patient is closely monitored by the care team for any infections, side effects etc. In case of an allogeneic transplant, doctors may prescribe medications to help prevent graft-versus-host disease (donor stem cells that now make up the new immune system see the body’s tissues and organs as foreign and attack them).
After the Bone Marrow Transplant
After the bone marrow transplant, the care team may recommend a clinical nutritionist to help create a healthy-eating plan that meets the patient’s needs and lifestyle. The nutritionist can also give dietary suggestions to control the side effects of chemotherapy and radiation, such as nausea. Some of the dietary recommendations may include:
- Avoid food and drinks that carry the risk of foodborne infections
- Avoid alcohol
- Eating a wide variety of healthy food gives the body nutrition it needs
- Limiting salt and sodium intake
The doctor may even recommend lifestyle changes, which may include:
- Avoid tobacco
- Keep the home clean and free of mold
- Limit time in sunlight because the skin may be more sensitive
- Regular physical activity to control weight, slowly increase physical activity as recovery happens
Range of Hematology Services
- Allogeneic stem cell transplant
- Autologous stem cell transplant
- Blood transfusion
- Cord blood transplant
- Day-care chemotherapy
- Myeloablative conditioning
- Outpatient transplant
- Reduced-intensity conditioning
Bone Marrow Transplant Unit - Fortis Hospital Mulund, Mumbai
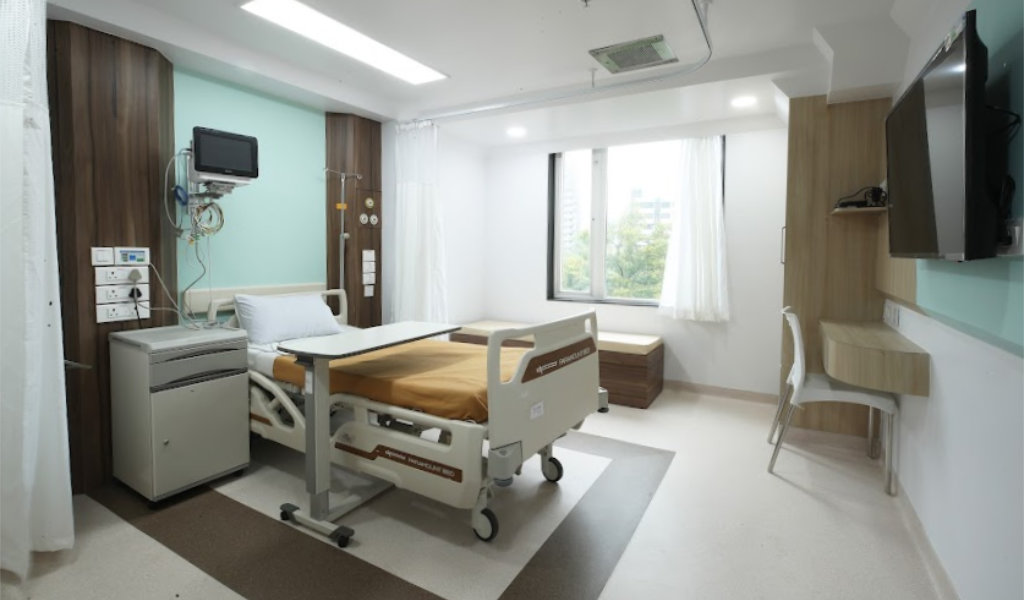
At Fortis Hospital Mulund, Mumbai, India we have access to modern equipment and the best healthcare facilities for Bone Marrow Transplant(BMT) patients across the globe.
Fortis Hospital Mulund, Mumbai, India
Address: Mulund Goregaon Link Road, Mulund-West, Mumbai, India 400078
Ph. 02268846143
Fortis Healthcare, best hospital in India stands at the forefront of medical excellence in India, offering unparalleled expertise in bone marrow transplants. Renowned for its state-of-the-art facilities and top-notch medical professionals, Fortis Hospitals provide comprehensive treatment for various diseases requiring bone marrow transplants. With advanced techniques and compassionate care, Fortis ensures optimal outcomes, making it the best choice for patients seeking superior healthcare at competitive costs.
Neurology Hospital in Mumbai | Kidney Transplant Hospital in Mumbai | Cancer Hospital in Mumbai | Bone Marrow Transplant Hospital in Mumbai | Heart Hospital in Mumbai | Breast Cancer Hospital in Mumbai | Mouth Cancer Hospital in Mumbai | Anemia Hospital in Mumbai | Heart Failure Treatment in Mumbai | Emergency Hospital in Mumbai | Radiation Therapy in Mumbai | Eye Hospital in Mumbai | Kidney Cancer Hospital in Mumbai
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | | Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Cancer Hospital in India | Best Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Oncology Hospital In India | Best Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal |
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery | Interventional Cardiology | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Neuro Physician | Gynecologist in Kolkata | Best Neurologist in India | Liver Transfer |
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- Haematology | Haematology | Paediatric Haematology and BMT
-
14 Years
-
2000
 Available at 1 different locations
Available at 1 different locations